DFHRS-Computation as Part of Geodetic Infrastructures for GNSS-Positioning Services (GIPS)
To enable the full spectrum of GNSS usability, the establishment and maintenance of
respective geodetic infrastructures for GNSS positioning services (GIPS) are
required worldwide
(see www.moldpos.eu).
Besides the geomonitoring component (GIPS-4) for GNSS-stations coordinate integrity
monitoring as well as for their use as early-warning and disaster mitigation
geomonitoring networks
(www.monika.ag,
www.goca.info),
GIPS has two transformation
components. Both transformation components concern the GNSS-consistent infrastructure
for spatial information (cadastre, GIS, urban planning, precise outdoor/indoor
navigation, construction, transportation, meteorology, land management, precise
agriculture, etc.).
The horizontal transformation component (GIPS-1) is related to the georeferencing of
spatial objects between the different modern regional ITRF-related frames (e.g. ETRF89
in Europe, SIRGAS in South America etc.) and the existing classical national reference
frames (fig. 5). GIPS-1 requires the establishment of respective datum-transformation
databases (see www.geozilla.de).
These databases enable the set up of RTCM transformation
messages (GIPS-3), and they can be for the used on GNSS controllers, in both cases as
infrastructure for GNSS-positioning services. Further these transformation-parameter
databases (GIPS-1) are needed interdisciplinarily in GIS-related applications.
The computation of HRS (Geoid N or QGeoid NQG) - as task of GIPS-2 -
enables by H = h – N
the conversion of ellipsoidal GNSS heights h to physical height H. GIPS-2
(www.dfhbf.de)
is therefore the second essential transformation component and modern spatial
infrastructure by enabling precise GNSS height-positioning in GNSS positioning services.
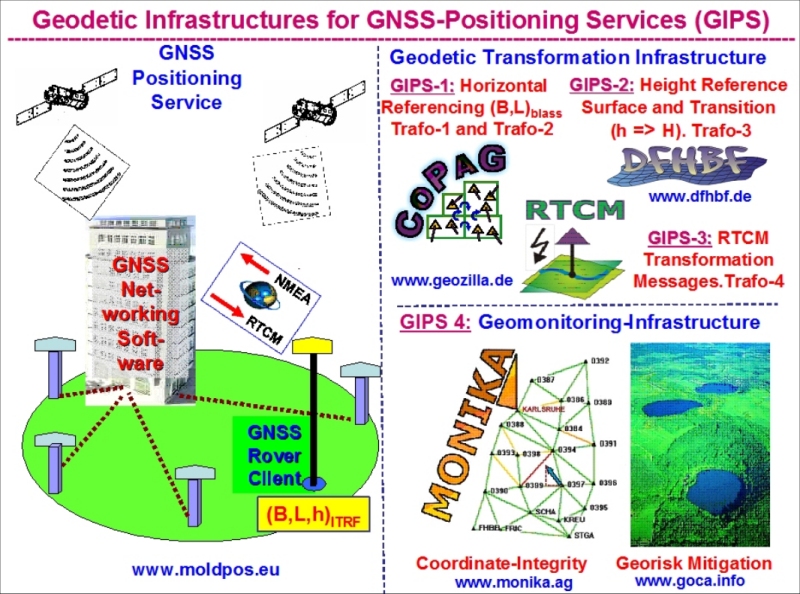
Fig. 5. Geodetic Infrastructures for GNSS Positioning Services (GIPS).

